Book Value And Fair Value Example
In this article we will discuss book value vs fair value in detail and indicate their key distinctions.
Book value and fair value example. At the end of 2 nd quarter was 4 443 million shares and the closing price of a share at that time was 247 74. Unlike book value investors don t have to wait for historical data to be able to derive a company s fair value and the fair value of the company at any given date will be accurate. Book value of assets is of relevance in historical cost method of accounting.
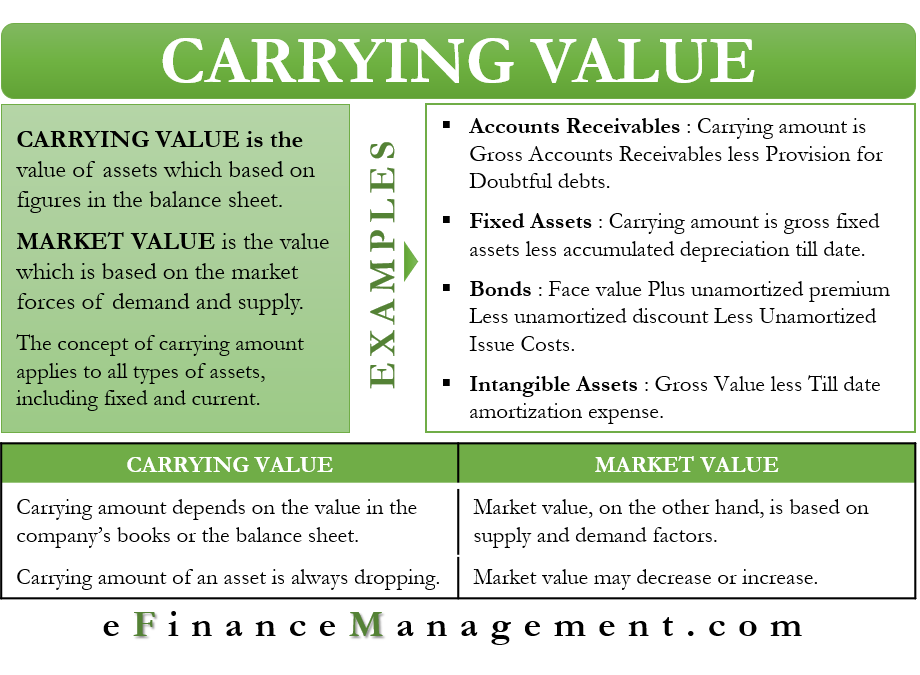
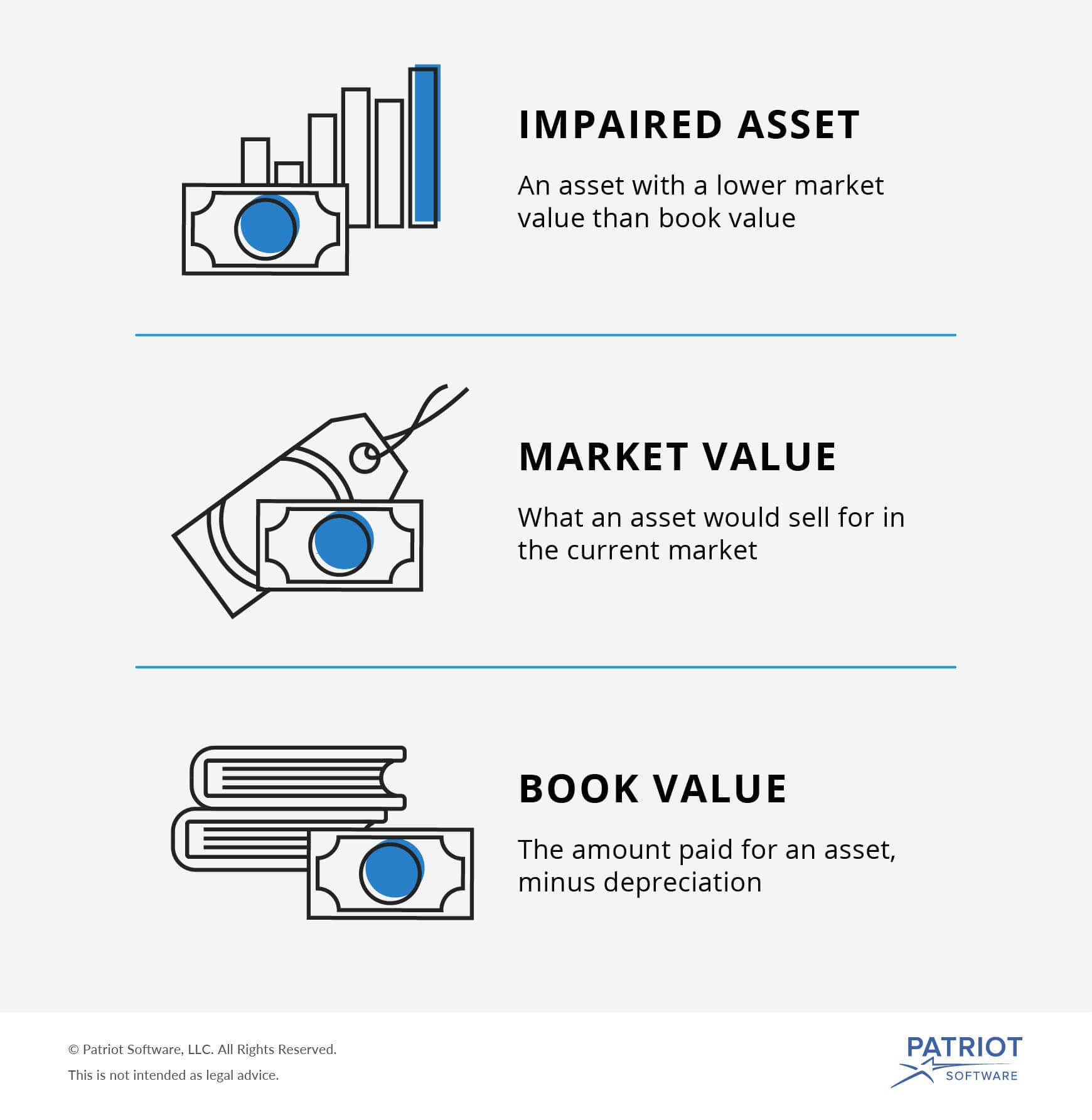
The two prices may or may not match depending on the type of asset. Book value usually represents the actual price that the owner paid for the asset. It is determined by deducting the accumulated depreciation of the asset as well as the impairment expenses goodwill impairment accounting goodwill is acquired and recorded in accounting when an entity purchases another entity for more than the fair market value of its.
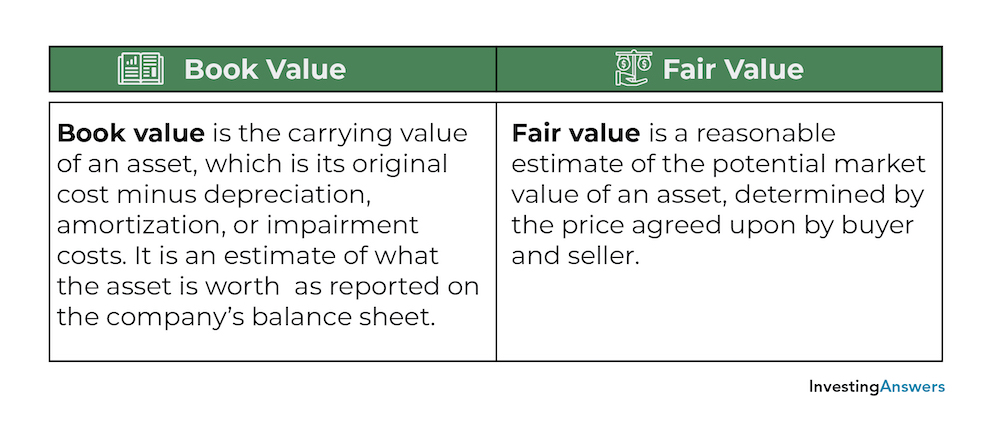
Book value indicates an asset s value that is recognized on the balance sheet. The difference between the book value and fair value is a potential profit or loss. Book value and fair value are both used to place a value on an asset but the difference lies in the way that price is determined.
Book value considers past or historical costs which have been recorded in the books of accounts at the time of occurrence of the transaction. Fair value of assets is of relevance in fair value method of accounting. Carrying value is also called book value which refers to the amount or value of an asset as it appears on the balance sheet.
Book value is the carrying value of an asset which is its original cost minus depreciation amortization or impairment costs. Typically fair value is the current price for which an asset could be sold on the open market. The carrying value or book value is an asset value based on the company s balance sheet which takes the cost of the asset and subtracts its depreciation over time the fair value of an asset is.